Read the article with FishingTheSpot: the american shad
Keep an eye on this subject!
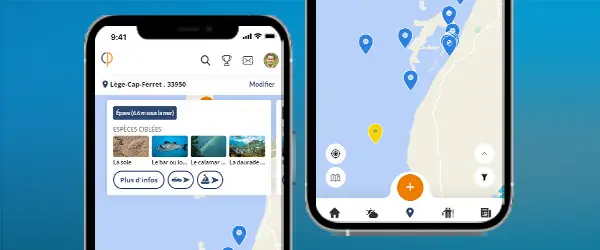
Thousands of species spotlights and techniques but also all the local information about your city!

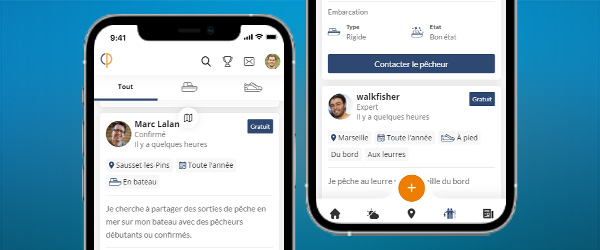

Meet other anglers near you and share your fishing fishing trips, afoot or on a boat, at sea or in freshwater
See the fishing tripsThe American Shad

spring
30 cm
Did you fish
this species this month?
The American Shad belongs to the Clupeidae family. With an average of 38 cm, adult specimens can measure up to 76 cm and weigh between 0.9 and 1.4 kg. It can live up to 13 years old. Egg laying takes place in May, June or July. On average, the female lays 140,000 eggs, but can reach 600,000 eggs. It is fished in the spring.
The American shad is characterized by its slender, high and very flattened body. The species has a very forked caudal fin and a low, elongated anal fin. It has no lateral line or adipose fin. Its color is silvery with a blue or blue-green sheen on the back and bright silver flanks. When entering fresh water for reproduction, the pigmentation may become darker, taking on a tan or copper hue, turning red for the head and belly parts. A black spot is visible near the top edge of the lid, sometimes followed by smaller spots. Its lower jaw fits into a notch in its upper jaw. It can also be recognized by its large scales that are easily detached. The ventral surface of the American shad is thin with saw tooth scales. With regard to internal characteristics, it has teeth in the premaxillary and lower jaw, a silver peritoneum and, between 53 and 59 vertebrae.
The American Shad lifestyle
During its migration to spawning grounds, this fish feeds very little or not at all. At sea, it feeds on plankton and other animals. In fresh water, young shad feed on related crustacean copepods and insect larvae.
Males are the first to arrive at the spawning river. When females succeed shortly thereafter, spawning will be accomplished under suitable conditions, particularly at temperatures of at least 12°C and from dusk. The peak of breeding activity occurs at temperatures near 18.3°C in May and June, or even until July in Canadian waters. The act occurs just below the surface of the water, the female accompanied by several males. The action of the spawners is visible by their vigorous swimming, which leaves a trace of foam. This nuptial parade cutting through the water is accompanied by particular sounds called splashing (literally these are the sounds emitted during "shad jumps"). The female releases her eggs in open water and this is how the males fertilize them.
The American Shad habitat
It is an anadromous species that can migrate over long distances. It is found mainly on the coasts, estuaries and rivers of the east coast of North America, from the St. Lawrence River in Quebec (Canada) to the St. John's River in Florida (United States). Specimens have been caught in Newfoundland waters and along the Labrador coast, but there is no evidence of potential breeding areas at these locations. They may therefore simply be individuals outside their usual range. It has also been introduced in several places, but with little success, except for introductions into the Sacramento and Columbia rivers on the west coast of North America. It is now found from the islands of Kamchatka (Siberia) and the Gulf of Cook (Alaska) to Baja California and Mexico. Only one population lives exclusively in fresh water, landlocked in Lake Millerton, California.
The American Shad angling
It is taken by light throw, heavy throw and fly. Rotating spoons are responsible for the majority of catches, although some flies also attract fish.