Read the article with FishingTheSpot: the scamp fih
Keep an eye on this subject!
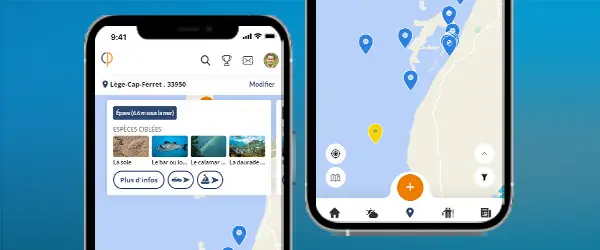
Thousands of species spotlights and techniques but also all the local information about your city!

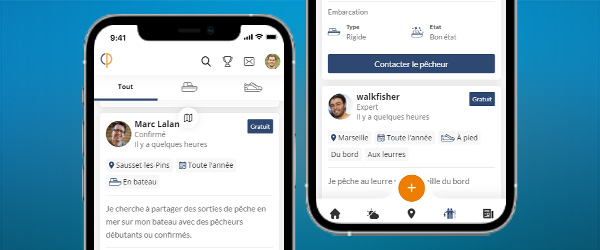

Meet other anglers near you and share your fishing fishing trips, afoot or on a boat, at sea or in freshwater
See the fishing tripsThe Scamp fih

all year round
50 cm
Did you fish
this species this month?
The scamp fish belongs to the Serranidae family. Its maximum size is 7.8 kg for more than 100 cm. It has a lifespan of about 48 years. It spawns from April to May. It can be fished all year round.
It has a light grey or brown color, large adults have elongated caudal rays and reddish brown spots on the sides that tend to be grouped in lines. It also has yellow spots around the corners of the mouth. It is linked to the gag and other slender groupers. Naughty animals are identified by their pronounced and pronounced dorsal and anal ray extensions, a more concave head profile and by their color. Scamps have a light brown to greyish brown body covered with well defined and separated black spots, which measure about 0.31 cm.
The Scamp fish lifestyle
The scamp is omnivorous. The scamp eats mainly other fish, but crustaceans and octopus are also common foods. A scamp can and will feed on anything he can hold in his mouth.
The Scamp are sexually mature at the age of 3 years or when they are over 40 cm. Like many grouper species, the scamp is a female specimen and turns into a male as it grows. The sexual transition occurs after females have reached sexual maturity and is spread over a wide range of sizes and ages, sometimes depending on the sex ratio in the population (an absence of large males may stimulate an earlier transition in females). Most fish under 60 cm in length are female. They generally migrate into the oceans, generally between spawning and feeding areas, as do tunas. Migration should be cyclical and predictable and cover more than 100 km. Spawning on reefs and wrecks from 9 to 60 meters deep.
The Scamp fish habitat
Found on high relief projections and rocky bottoms in the eastern Gulf of Mexico; in the low bottoms, between 30 and 100 m deep, from North Carolina to Georgia; this species was the most abundant grouper in areas of living Octolina coral formations located between 70 and 100 m deep off the east coast of Florida. This species apparently moved towards shore when the bottom temperature dropped below 8.6°C. Juveniles found in shallow waters at piers and in mangrove areas. Sometimes quite close to shore, but generally confined to deep reefs and offshore edges. Coastal juveniles are found in estuaries and bays, adults in deeper coastal and offshore waters, in reefs, wrecks, jetties and pilings up to 91 m deep.
The scamp fish angling
It can be caught with Hook and line, and long line. It can also caught with drift fishing.