Read the article with FishingTheSpot: the tarpon
Keep an eye on this subject!
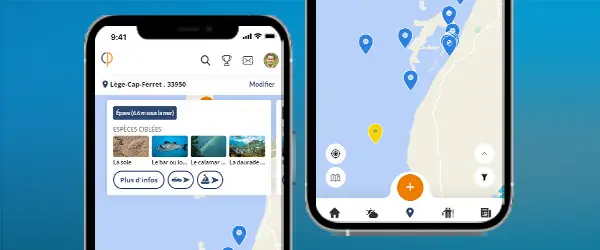
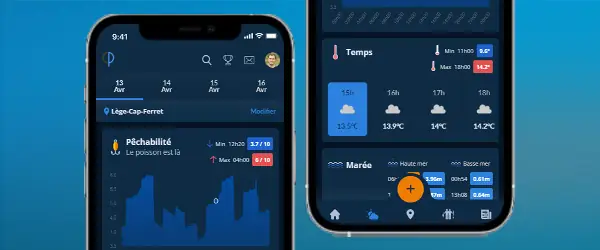
Thousands of species spotlights and techniques but also all the local information about your city!

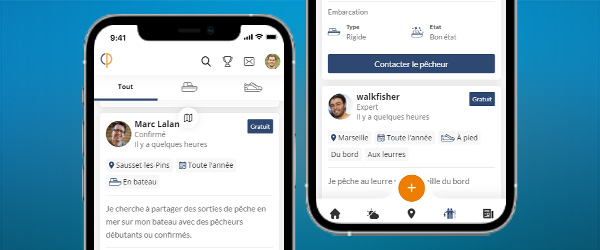

Meet other anglers near you and share your fishing fishing trips, afoot or on a boat, at sea or in freshwater
See the fishing tripsThe Tarpon

May to July
less than 100 cm
Did you fish
this species this month?
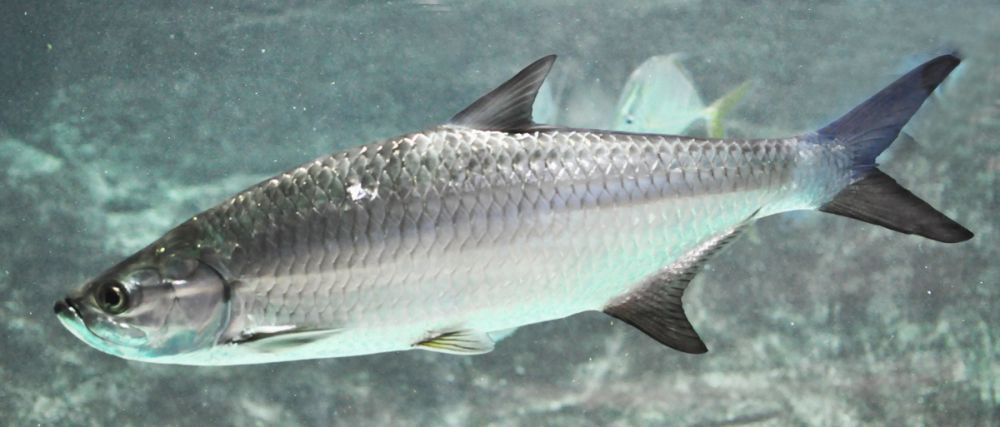
The Tarpon belongs to the Megalopidae family. The female tarpon can reach more than 2.5 m in length and weigh nearly 161 kg, the males being generally smaller. Males live longer than 30 years, while females can live longer than 50 years. They breed from May to July. It is generally fished during the spawning season.
Externally, the almost vertical silvery sides made of large scales are the most distinctive feature of the tarpon. The tarpon has an upper mouth and the lower mandible extends well beyond the gape. The fins do not contain thorns, but are all made of soft rays. The dorsal fin is high forward and contains 13-15 rays of light, the last ray of which is very elongated into a thick filament. The caudal is deeply forked and the lobes appear to have the same length. The anterior part of the anal fin is deep and triangular. The fin has 22-25 rays, the last ray being elongated again as in the dorsal fin, but shorter and present only in adults. The tarpon has large pelvic fins and long pectoral fins containing 13 to 14 soft rays. The name "silver king" refers to the predominant bright silvery color on the sides and belly of the tarpon. Dorsally, the tarpon usually appears from dark blue to greenish black. However, the color may appear brownish or coppery for individuals living in inland waters. Dorsal and caudal fins have dark edges and often appear dark.
The Tarpon lifestyle
Their eating habits and diet depend on age. As a young animal, it feeds on zooplankton, small fish and insects. The adult feeds on invertebrates, shrimps and larger crabs.
Its fertility is about 12 million eggs. They make significant migrations to offshore spawning areas, where currents then bring larvae to coastal nurseries. Tarpon reaches sexual maturity at the age of 6 or 7 years.
The Tarpon habitat
Tarpons inhabit a wide variety of habitats, but are found mainly in coastal waters, bays, estuaries and lagoons bordered by mangroves in tropical, subtropical and temperate climates. Normal habitat depth extends to 30 m.
It can be found on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. In the western Atlantic, fish inhabit mainly the warmer coastal waters concentrated around the Gulf of Mexico, Florida and the Caribbean. However, tarpons are not uncommon north of Cape Hatteras and their extreme extent extends from Nova Scotia in the north, to Bermuda, and Argentina in the south. Tarpons have been discovered at the Panama Canal Terminal and around Coiba Island in the Pacific.
The Tarpon angling
They can be caught on hook and line.